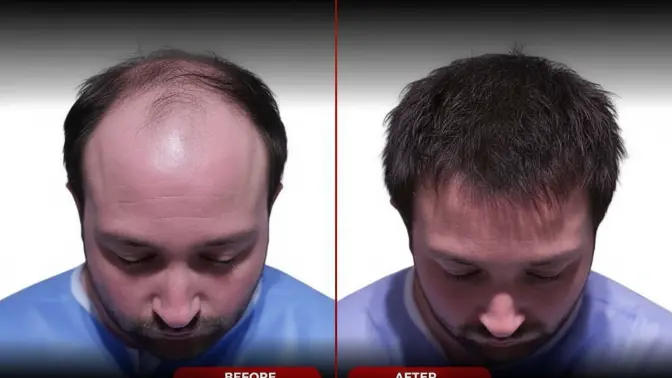
Hair Transplant Complications: Prevention and Management Guide

Learn about potential hair transplant complications, how to prevent them, and what to do if issues arise. Comprehensive guide to ensuring safe recovery and optimal results from your hair restoration procedure.
Hair transplant procedures are generally safe when performed by experienced surgeons, but like any surgical procedure, they carry some risks. Understanding potential complications, how to prevent them, and what to do if issues arise is crucial for anyone considering or recovering from a hair transplant. This comprehensive guide covers common complications, prevention strategies, and proper management to ensure optimal recovery and results.
COMMON COMPLICATIONS AND RISKS
While serious complications are rare with modern FUE techniques, some issues can occur. Common complications include infection, bleeding, swelling, scarring, poor graft survival, and numbness. Most of these are minor and resolve with proper care, but understanding them helps you recognize when to seek medical attention. The risk of complications is significantly reduced when procedures are performed by experienced surgeons in sterile environments with proper protocols.
INFECTION PREVENTION
Infection is one of the most serious potential complications, though it's rare with proper protocols. Prevention starts with choosing a clinic that maintains strict sterile conditions. Post-operatively, following your surgeon's instructions for wound care is crucial. This includes proper washing techniques, keeping the area clean and dry, and taking prescribed antibiotics if recommended. Signs of infection include excessive redness, pus, fever, or increasing pain—if you notice these, contact your surgeon immediately.
BLEEDING AND SWELLING
Minor bleeding and swelling are normal in the first few days after surgery. Bleeding typically stops within hours, and swelling usually peaks around day 3-4 before gradually subsiding. To minimize swelling, keep your head elevated, especially when sleeping. Apply cold compresses as instructed, and avoid activities that increase blood pressure. If bleeding is excessive or doesn't stop, or if swelling is severe and accompanied by other symptoms, contact your surgeon.
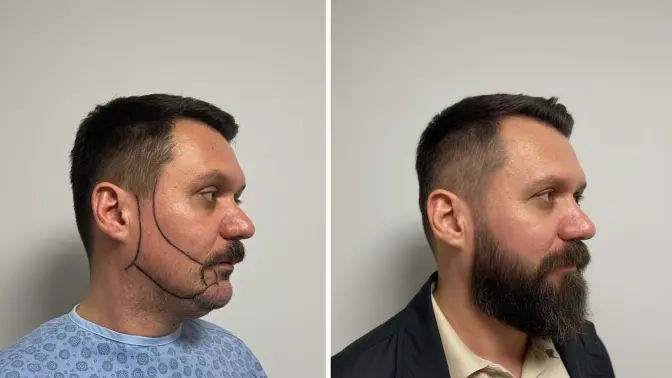
GRAFT SURVIVAL AND FAILURE
Graft survival rates are typically 90-95% with modern techniques, but some graft loss can occur. Poor graft survival can result from improper handling during surgery, trauma to grafts post-operatively, or underlying health issues. Following aftercare instructions meticulously is crucial—avoid touching, scratching, or picking at the transplanted area. Protect grafts from trauma, and don't engage in activities that could dislodge them. Most graft loss occurs in the first few days if it's going to happen.
SCARRING CONSIDERATIONS
FUE techniques minimize scarring compared to older methods, but some scarring is inevitable. In the donor area, tiny white dots may be visible, though they're usually undetectable once hair grows back. In the recipient area, scarring is minimal and typically not visible. Proper technique, avoiding over-harvesting, and following aftercare instructions help minimize visible scarring. Patients with a history of keloid scarring should discuss this with their surgeon beforehand.
"Prevention is always better than treatment. Choosing an experienced surgeon and following aftercare instructions meticulously significantly reduces the risk of complications."
NUMBNESS AND SENSATION CHANGES
Temporary numbness in the donor and recipient areas is common after surgery due to nerve disruption during the procedure. This typically resolves within weeks to months as nerves regenerate. Permanent numbness is rare but can occur. Most patients regain normal sensation, though it may take several months. If numbness persists beyond 6 months or is accompanied by other symptoms, consult your surgeon.
PRE-OPERATIVE PREVENTION
Many complications can be prevented through proper pre-operative preparation. This includes disclosing your complete medical history, current medications, and any allergies. Follow pre-operative instructions regarding medications to avoid (like blood thinners), smoking cessation, and alcohol restrictions. Ensure you're in good health before surgery, and address any underlying medical conditions. Choosing an experienced, board-certified surgeon in a reputable clinic is perhaps the most important prevention measure.
WHEN TO SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION
While most post-operative issues are normal, certain symptoms require immediate medical attention. These include signs of infection (fever, excessive redness, pus), excessive bleeding that doesn't stop, severe pain not relieved by prescribed medications, or any unusual symptoms that concern you. Don't hesitate to contact your surgeon with questions or concerns—early intervention can prevent minor issues from becoming serious complications.